景颐新闻详情
Introduction to UV visible diffuse reflection
Diffuse light refers to the light from a light source that enters the sample and returns to the sample surface after multiple reflections, refractions, scattering and absorption. Its diffuse reflection spectrum is mainly related to the electronic structure of the material.
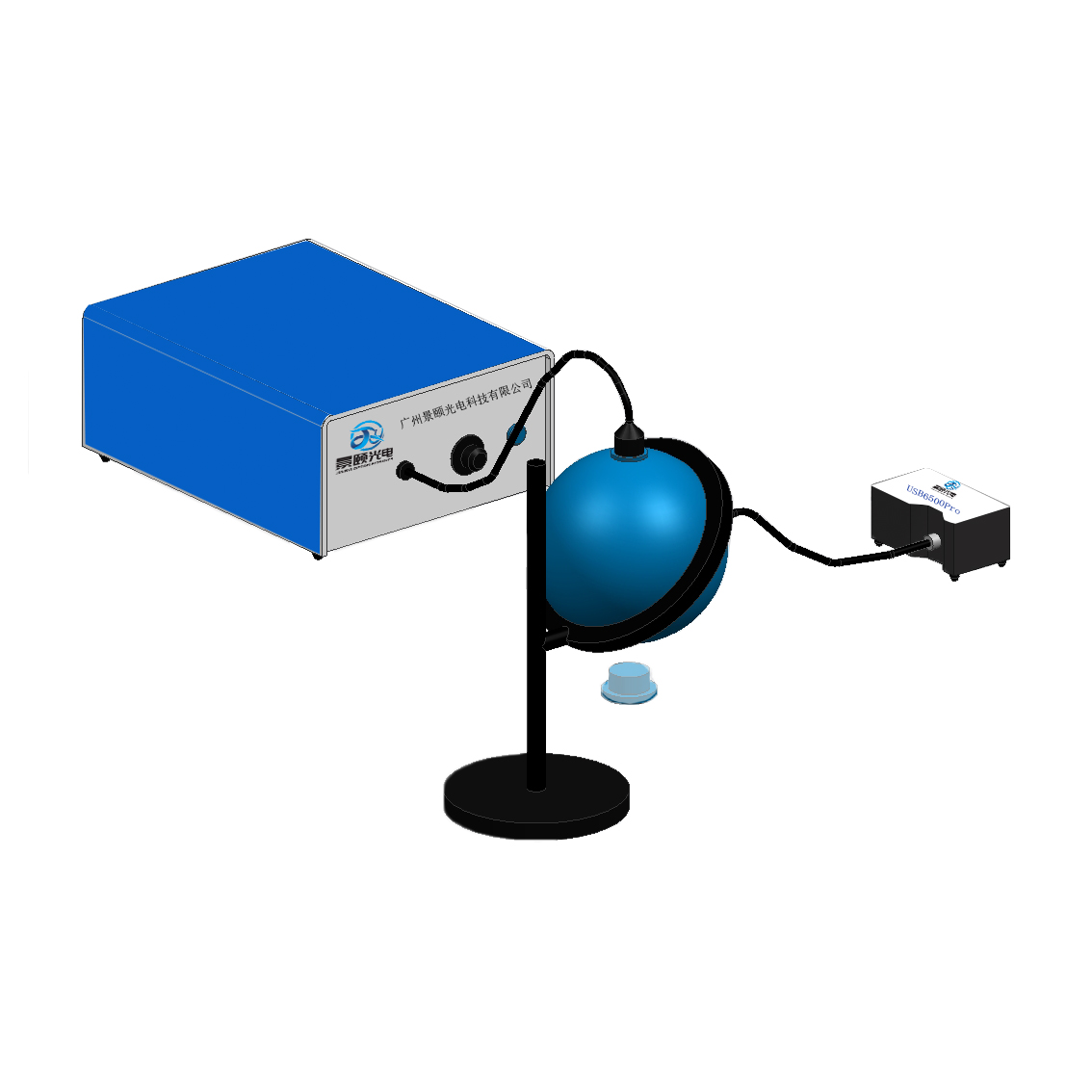
For opaque samples such as powdery materials, it is impossible to test them with a direct light system. To further understand their performance, it is necessary to test the diffuse reflected light with the help of an integrating sphere. Diffuse light is the light formed by the interaction of molecules in the sample, which carries rich information about the electronic structure and organization of the sample.
For the test of turbid solution, suspended solution, irregular lens and other samples, if the direct light system is used for the test, the shape and size of the light spot arriving at the detector will change due to the light scattering or light path change when passing through the sample, and the test results will produce errors. In order to solve the inaccurate test caused by the light path shift and beam change, it is necessary to use an integrating sphere to collect at this time, The multiple diffuse reflection of the signal light in the integrating sphere will cause the error of the measurement results. In order to solve the inaccurate test caused by the optical path deviation and beam change, the integrating sphere is needed to collect the signal light at this time. The signal light will be measured in a constant ratio after multiple diffuse reflections in the integrating sphere.
Brief Introduction of Semiconductor Bandgap Width
At room temperature, semiconductors are materials with conductivity between conductors and insulators, and have a certain band gap. By using appropriate light to excite semiconductor materials, it can excite electrons in the valence band to the conduction band, resulting in electron-hole pairs, and the energy difference between the low end of the conduction band and the top of the valence band is the size of the band gap. The band structure of semiconductor can be measured to analyze its photoelectric characteristics. UV-Vis DRS is a method to analyze the band gap value.
An example of UV-visible diffusion and band gap calculation
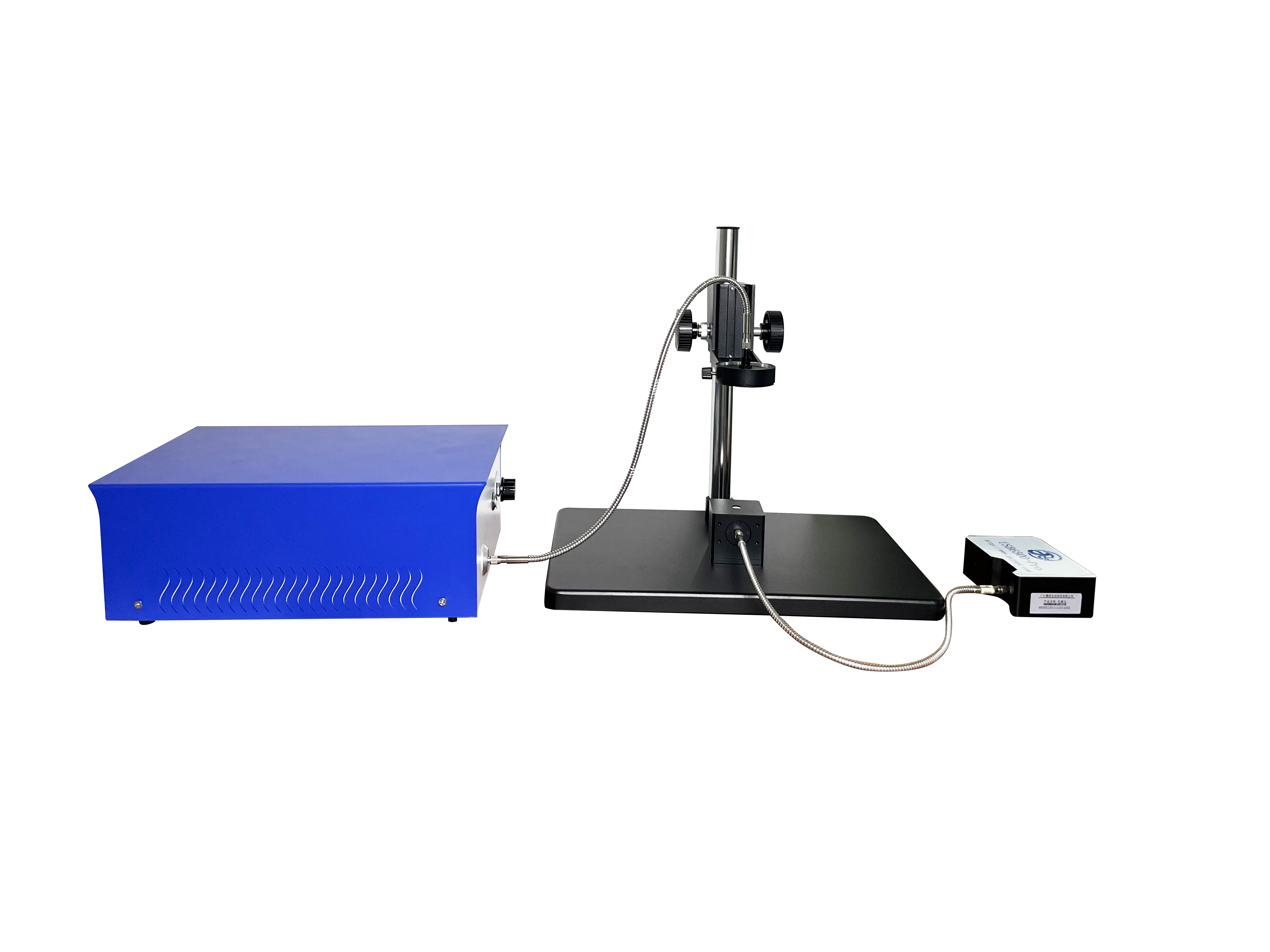
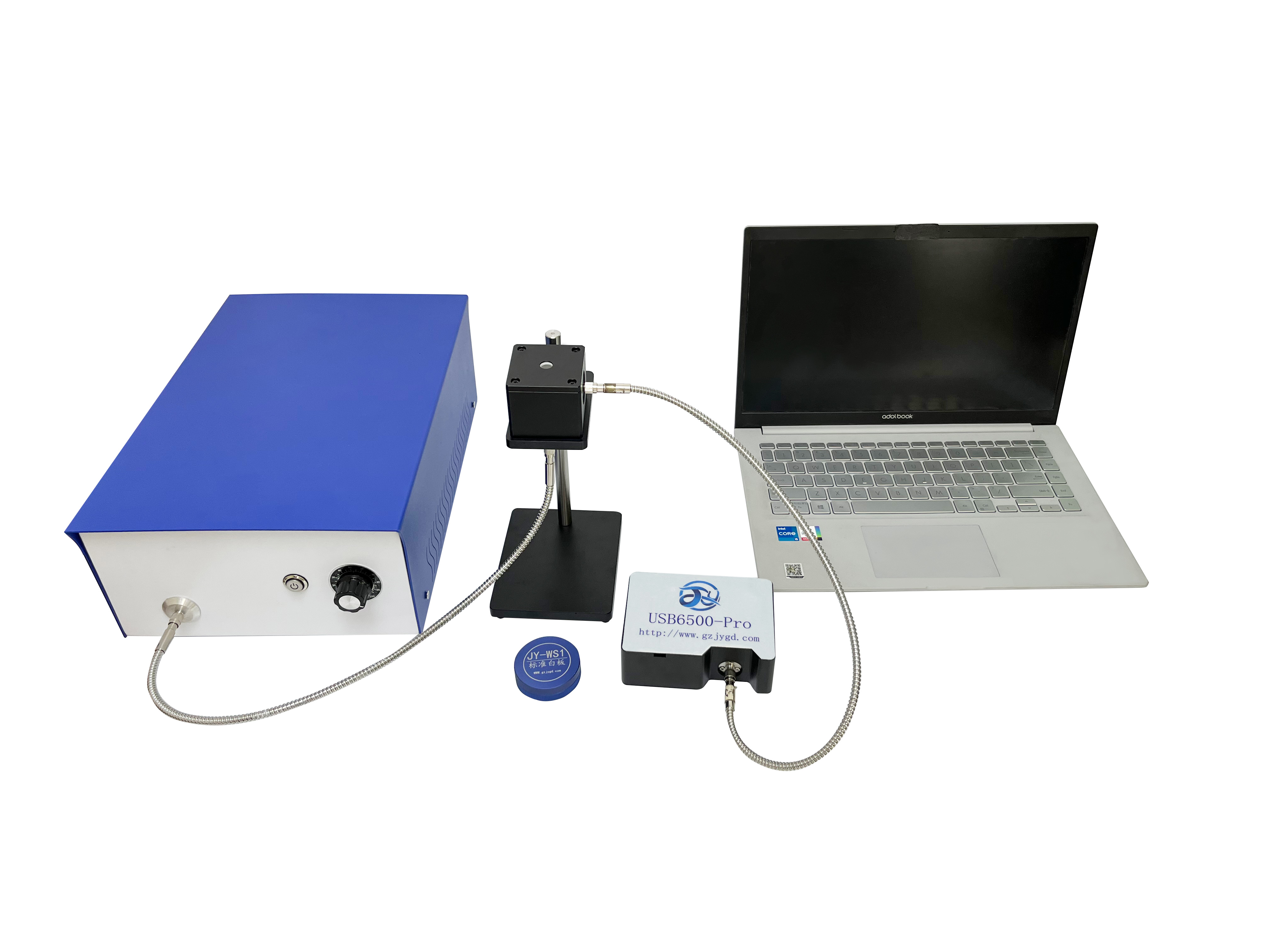
This paper takes the powder sample as an example, and uses the Tianmei UV2600 UV-visible spectrophotometer and IS2600 integrating sphere to test. The integrating sphere cell has two groove designs, positive and negative, which meet the requirements for the test of conventional sample size and micro sample size respectively. In addition, the powder cell has a quartz window, which avoids the pollution caused by the sample powder falling into the instrument or the integrating sphere.
First, take the standard white board (R% mode) as the baseline test, and then conduct the diffuse reflection test on the sample to obtain its UV-visible diffuse reflection spectrum.
It can be seen from the diffuse reflection law, also known as Kubelka – Munk function:
F (R)=(1- R)2/2 R= K/S
R, K and S represent the reflection coefficient, absorption coefficient and scattering coefficient of the sample respectively
In addition, according to a formula put forward by Tok, Davis and Mott, it is usually called "Tok formula":
(h ρ*α) n= A (h ε- Eg)
In these two functions, h is Planck constant, ρ Is frequency, A is constant, α Is the absorption index, and Eg is the semiconductor band gap width
Here n is n=1/2 for indirect bandgap semiconductors and n=2 for direct bandgap semiconductors
F (R ∞) proportional absorption coefficient α, and α F (R ∞) can be substituted in Tauc equation, so it can be converted into:
[F(R)*hv]n = A(hv - Eg)
Then, hv is the abscissa and (F (R ∞) * hv) n is the ordinate. When (F (R ∞) * hv) n=0, the corresponding abscissa hv is the size of the Eg value. The following is an example of a direct semiconductor material:
Examples of specific data processing methods:
According to UV-Vis DRS data (wavelength and ordinate are reflectivity respectively), as shown in the following table:
This will be converted to column D data: hv=1240/wavelength, in eV
Therefore, convert a ordinate to column F data, F (R ∞)=(1 - R) 2/2 R, where R represents the reflectance value, that is, column B/100 in the table
The graph of ordinate and abscissa can be obtained from the table data, and the intersection point of the line extrapolation and abscissa is the Eg value.
conclusion
The above example shows that the width limit of the semiconductor material is calculated by using the Tianmei UV-visible spectrophotometer UV2600+integrating sphere IS2600, the diffuse reflection test of the semiconductor material is performed by using the Tianmei UV-visible spectrophotometer UV2600+integrating sphere IS2600+, and the electronic structure information and light absorption test of the material are reflected.